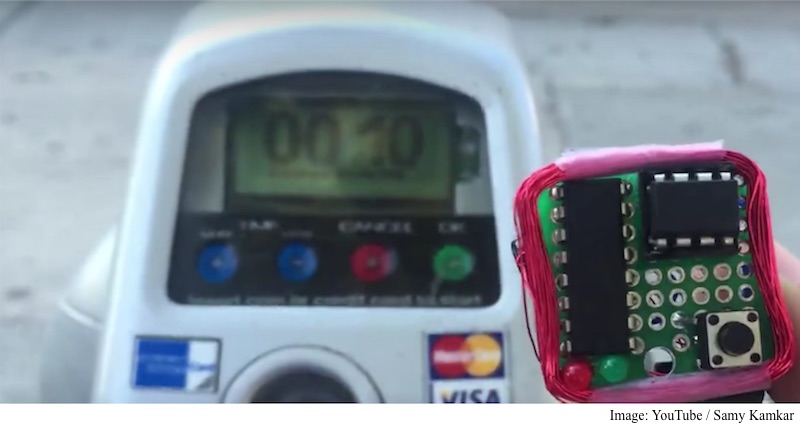

A poor security implementation by American Express has made it possible for attackers to accurately predict the number of a user’s next American Express credit card, and also figure out the expiration date of that card. A hacker has developed a device called MagSpoof, which is being sold for $10 (roughly Rs 650) and can let anyone exploit this vulnerability.
Samy Kamkar’s MagSpoof can steal new credit card numbers as fast as American Express could generate them, he claims. The renowned hacker first observed this vulnerability when he lost his American Express card four months ago, and noticed a pattern in the credentials on his replacement American Express card.
“I pulled up the numbers to several other Amex cards I had, and then compared against more than 20 other Amex cards and replacements and found a global pattern that allows me to accurately predict American Express card numbers by knowing a full card number, even if already reported lost or stolen,” he wrote in a blog post.
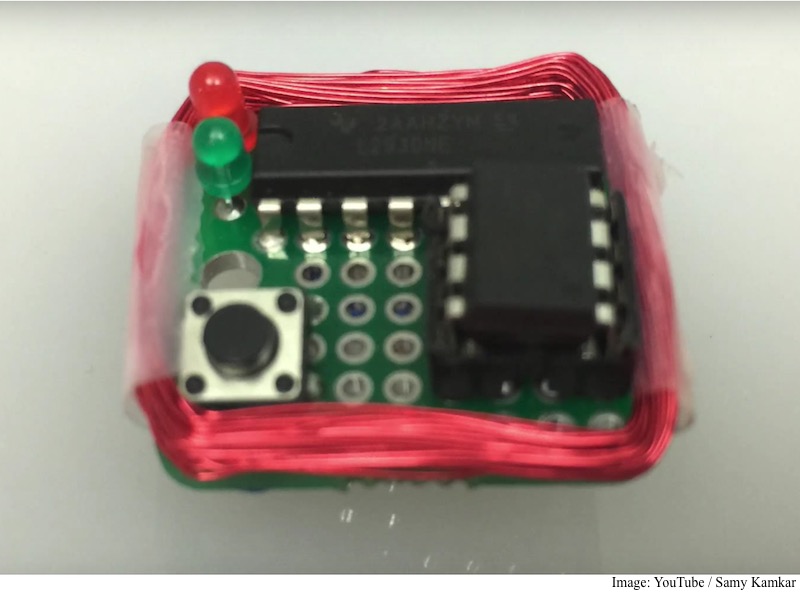
That isn’t all. The watch-sized MagSpoof emits an electromagnetic field strong enough to hit a credit card reader’s sensor from close proximity. It then sends a signal to trick point-of-sale readers into accepting payment from the device. The PoS devices, also known as chip-and-PIN readers and EVM, are designed to read cards that have a microchip with cryptographic encryption.
The security implications of getting the card “formula” out or a criminal getting their hands on the MagScoop device is that they can figure out the victim’s next card number even before the victim receives it. This will allow the fraudster to use the victim’s credentials to do transactions. Kamkar says that part of the reason he is exposing the vulnerability is to prove American Express wrong, which found his findings not a “major issue” when notified four months ago.
Kamkar said that he also studied the magnetic stripe on the back of payment cards to figure out how they work. He found a vulnerability that could allow him to manipulate the code the stripes sent to again fool PoS devices. He hasn’t disclosed the vulnerability but has released the schematics and software for MagSpoof.
[“source-gadgets.ndtv”]
